
| Catalog Number | Product | Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3028 | Human LILRA6-CHO-K1 Stable Cell Line | 2 vials | $4950 | Order |
| Catalog Number | C3028 |
|---|---|
| Cell Line Name | Human LILRA6-CHO-K1 Stable Cell Line |
| Accession Number | NM_001360167.1 (Full-length cDNA) |
| Host Cell | Adherent CHO-K1 |
| Quantity | Two vials of frozen cells (1x106 per vial) |
| Culture Medium | DMEM with 10% FBS, 4 ug/ml puromycin |
| Freezing Medium | 90% FBS and 10% DMSO |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen upon receipt |
| Product Datasheet: | Download PDF |
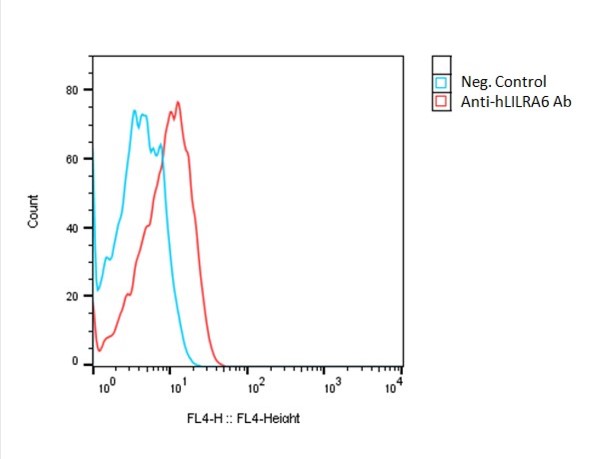
Detection of human LILRA6 expression on human LILRA6-CHO-K1 cells using a APC-anti-human LILRA6 antibody (R&D Systems #FAB8656A)
LILRA6 (Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor A6) is a member of the LILR (Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor) family of proteins. It is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein and has an extracellular domain composed of two Ig-like domains followed by a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail. LILRA6 is primarily expressed on the surface of immune cells such as monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells. It contains both activating and inhibitory domains and plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses and inflammation. Studies have shown that LILRA6 is involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer. LILRA6 expression is upregulated in some cancers, such as glioblastoma, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer, and is associated with poor prognosis. LILRA6 may contribute to tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis by modulating the activity of immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. Given its role in immune regulation and its expression in some cancers, LILRA6 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for cancer immunotherapy. Blocking LILRA6 signaling may enhance the antitumor activity of immune cells and improve treatment outcomes.
Truong AD, Rengaraj D, Hong Y, Tran HTT, Dang HV, Nguyen VK, Lillehoj HS, Hong YH. Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors A2 and A6 are Expressed in Avian Macrophages and Modulate Cytokine Production by Activating Multiple Signaling Pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 19(9):2710. 2018.
Hirayasu K, Arase H. Functional and genetic diversity of leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor and implication for disease associations. J Hum Genet. 60(11):703-8. 2015.