
| Catalog Number | Product | Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3068 | Mouse-EpCAM-CHO-K1 Stable Cell Line | 2 vials | $3950 | Order |
| Catalog Number | C3068 |
|---|---|
| Cell Line Name | Mouse-EpCAM-CHO-K1 Stable Cell Line |
| Accession Number | NP_032558.2 |
| Host Cell | Adherent CHO-K1 |
| Quantity | Two vials of frozen cells (2x106 per vial) |
| Culture Medium | DMEM with 10% FBS, 4 µg/ml puromycin |
| Freezing Medium | 90% FBS and 10% DMSO |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen upon receipt |
| Product Datasheet: | Download PDF |
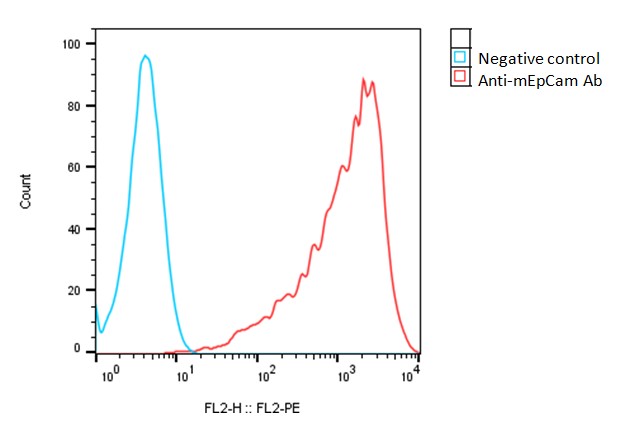
Detection of mouse EpCAM expression on mEpCAM-CHO-K1 stable cells using a PE-anti-mEpCAM antibody (BioLegend, Cat. #329907)
EpCAM, short for Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule, is a transmembrane protein, with an extracellular domain involved in cell-cell adhesion and intracellular domains participating in signal transduction. It’s expressed in epithelial tissues throughout the body including the linings of organs like skin, intestines, liver, pancreas and various glands. In homophilic cell-cell adhesion, it binds to other EpCAM molecules on neighboring cells facilitating cell-cell interactions to help maintain tissue integrity, embryonic development, and tissue regeneration. EpCAM is known to regulate various signaling pathways, including the Wnt signaling pathway, which is crucial for cell proliferation and differentiation. EpCAM has garnered significant attention in cancer research due to its overexpression in various malignancies. It’s overexpression in many cancers, including colorectal, breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and lung cancers is often associated with increased tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Therefore, EpCAM serves as a valuable biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of certain cancers.
Huang L, Yang Y, Yang F, et al. Functions of EpCAM in physiological processes and diseases (Review). Int J Mol Med. 42(4):1771-1785. 2018.
Eyvazi S, Farajnia S, Dastmalchi S, Kanipour F, Zarredar H, Bandehpour M. Antibody Based EpCAM Targeted Therapy of Cancer, Review and Update. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 18(9):857-868. 2018.