
| Catalog Number | Product | Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3095 | Mouse PD-1-CHO-K1 stable cell line | 2 vials | $3950 | Order |
| Catalog Number | C3095 |
|---|---|
| Cell Line Name | Mouse PD-1-CHO-K1 stable cell line |
| Accession Number | NM_008798.3 |
| Host Cell | Adherent CHO-K1 |
| Quantity | Two vials of frozen cells (2x106 per vial) |
| Culture Medium | DMEM with 10% FBS, 4 µg/ml puromycin |
| Freezing Medium | 90% FBS and 10% DMSO |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen upon receipt |
| Product Datasheet: | Download PDF |
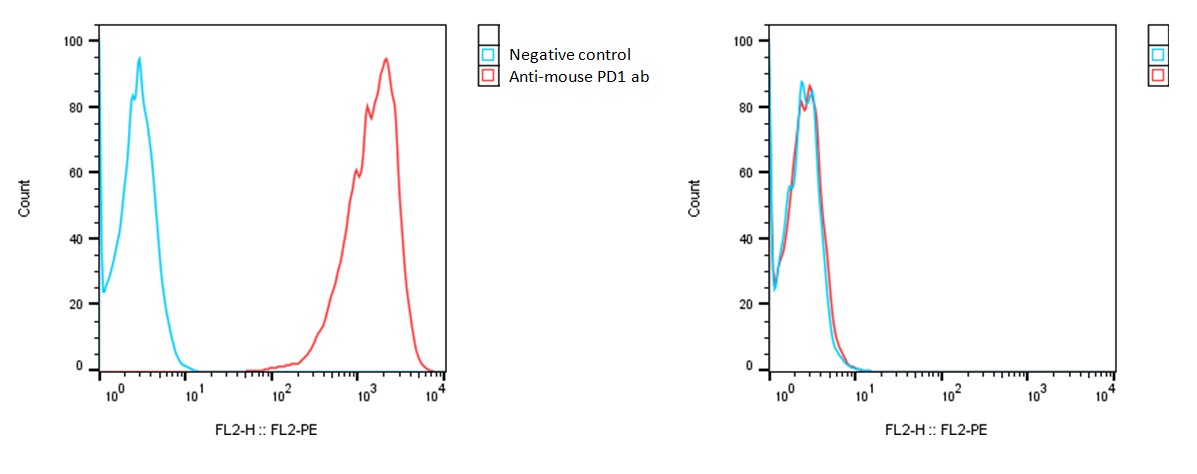
Detection of mouse PD-1 expression on mouse PD-1-CHO-K1 stable cells (A) and Vector Control-CHO-K1 (B) using a monoclonal antibody specific for mouse PD-1 (eBioscience #12-9985-81)
PD-1 (Programmed Cell Death Protein 1) is a cell surface receptor protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. PD-1 is primarily expressed on the surface of activated T cells, B cells, natural killer cells (NK cells), and monocytes. The primary function of PD-1 is to inhibit T-cell activation and effector functions. When PD-1 interacts with its ligands, PD-L1 (Programmed Death-Ligand 1) and PD-L2 (Programmed Death-Ligand 2), which are expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and certain non-immune cells, it sends inhibitory signals to T cells. This inhibitory signaling pathway helps prevent autoimmune responses and limits collateral damage to healthy tissues during immune responses. Many cancer cells upregulate PD-1 and its ligands inhibiting T cell activity thus, creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment allowing cancer cells to thrive and escape immune destruction. PD-1 and its associated pathway have emerged as a promising therapeutic target in the field of cancer immunotherapy. PD-1 inhibitors have shown great success in treating cancer by blocking PD-1’s interaction with its ligands, T cells can recognize and attack cancer cells correctly.
Chen DS, Irving BA, Hodi FS. Molecular pathways: next-generation immunotherapy—inhibiting programmed death-ligand 1 and programmed death-1. Clin Cancer Res. 18(24):6580-6587. 2012.
Hargadon KM, Johnson CE, Williams CJ. Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for cancer: An overview of FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol. 62:29-39. 2018