
| Catalog Number | Product | Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3008 | Human CLDN18.1-FLAG-CHO-K1 Stable Cell Line | 2 vials | $4950 | Order |
| Catalog Number | C3008 |
|---|---|
| Cell Line Name | Human CLDN18.1-Flag-CHO-K1 Stable Cell Line |
| Accession Number | Full-length human CLDN18.1 (NP_057453) |
| Host Cell | Adherent CHO-K1 |
| Quantity | Two vials of frozen cells (1x106 per vial) |
| Culture Medium | DMEM with 10% FBS, 4ug/ml puromycin |
| Freezing Medium | 90% FBS and 10% DMSO |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen upon receipt |
| Product Datasheet: | Download PDF |
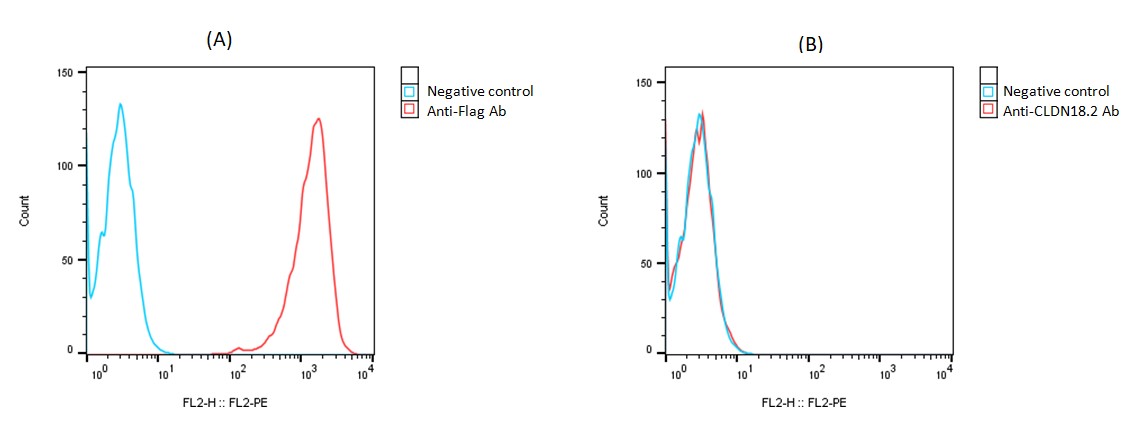
A. Detection of human CLDN18.1 expression on CHO-K1/Human CLDN18.1 cells using a mouse monoclonal antibody specific for the Flag tag. (Cat. #A1001)
B. Detection of human CLDN18.2 expression on CHO-K1/Human CLDN18.1 cells using a human monoclonal antibody specific for human CLDN18.2. (Cat #A1008) No CLDN18.2 is detected on the cells.
Claudin-18 (CLDN18) is a member of a large family of four-span transmembrane proteins called Claudins. These proteins are the essential components of the mammalian tight junctions (TJs) in epithelial cells. Claudin-18 has two splice variants, 18.1 and 18.2. While CLDN18.1 is specifically expressed in the lung tissue, CLDN18.2 expression in normal tissue is more restricted and is only detected in small patches of stomach mucosal. CLDN18.2 expression is elevated in many types of epithelial cancers including stomach, esophagus, pancreatic and ovarian cancers. The expression of CLDN18.2 is not only detected in primary tumors, but also in the metastatic sites. Therefore, CLDN18.2 is an ideal target for monoclonal antibody-based cancer therapies.
Tureci O. et al. Claudin-18 gene structure, regulation, and expression is evolutionary conserved in mammals. Gene. 481(2): 83-92. 2011.
Sahin U. et al. Claudin-18 Splice Variant 2 Is a Pan-Cancer Target Suitable for Therapeutic Antibody Development. Clin. Cancer Res. 14(23):7624-7634. 2008.
Niimi T. et al. Claudin-18, a Novel Downstream Target Gene for the T/EBP/NKX2.1 Homeodomain Transcription Factor, Encodes Lung- and Stomach-specific Isoforms Through Alternative Splicing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21(21): 7380-7390. 2001.